What is Kubernetes? An Introduction to Container Orchestration
Hey there! If you’ve been anywhere near the tech world lately, you’ve probably heard about Kubernetes. It’s one of those buzzwords everyone seems to be talking about, especially if you’re dealing with cloud computing or DevOps. But what exactly is Kubernetes, and why is everyone so excited about it?
In this article, we’ll break down Kubernetes in simple terms, without all the technical jargon, so you can get a clear understanding of what it is, how it works, and why it’s so important in today’s tech world. Whether you’re a developer, IT enthusiast, or just curious about the latest tech trends, this article is for you!
What Exactly is Kubernetes?
At its core, Kubernetes (often abbreviated as K8s) is an open-source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and operation of application containers. Imagine having hundreds or even thousands of containers (mini virtual environments for your applications) and trying to manage them all manually—it would be a nightmare, right? That’s where Kubernetes comes in.
Kubernetes acts like a conductor in an orchestra, ensuring that all the containers in your system are working together in harmony. It makes sure that the right containers are running, they have the necessary resources, and they are efficiently distributed across different environments, like multiple servers or cloud platforms.
Why Do We Need Kubernetes?
Let’s face it: managing software applications, especially in today’s cloud-based world, can get complicated—really complicated. As companies started adopting containers (like Docker) to package their applications, it became clear that manually handling these containers was simply not sustainable. Enter Kubernetes.
Here are some key reasons why Kubernetes is such a game-changer:
- Scalability: Kubernetes allows you to scale your applications up or down effortlessly based on the traffic or demand.
- Automation: Forget manually restarting failed containers—Kubernetes automates that process for you. It also handles tasks like load balancing and resource allocation.
- Multi-cloud Support: Kubernetes can run on any cloud platform—AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, or even your own private servers.
- Self-healing: Kubernetes continuously monitors the health of your containers and restarts them if something goes wrong.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Kubernetes ensures that your containers use resources efficiently, preventing wastage and reducing costs.
How Does Kubernetes Work?
Now, let’s dive a little deeper into how Kubernetes actually works under the hood. Don’t worry, I’ll keep it as simple as possible!
Kubernetes has a bunch of components, but the most important ones are:
- Nodes: These are the machines (virtual or physical) where your containers run. Kubernetes clusters are made up of multiple nodes.
- Pods: A pod is the smallest unit in Kubernetes. It contains one or more containers that are deployed together. Pods share resources like network and storage.
- Cluster: A cluster is a group of nodes managed by Kubernetes. It’s the foundation on which everything runs.
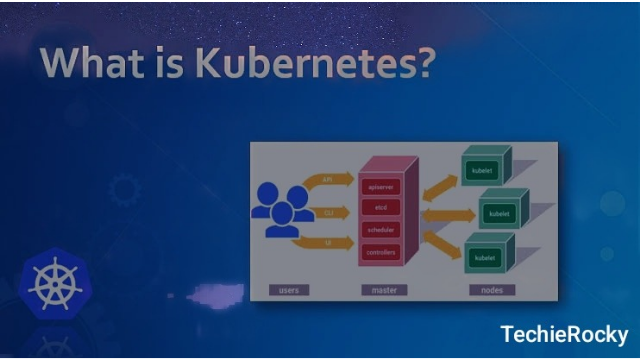
- Master Node: This is the brain of your Kubernetes cluster. It controls and manages the worker nodes, ensuring the right containers are running at the right time.
- Scheduler: This component ensures that containers are scheduled to run on the right nodes based on their resource requirements and the available resources in the cluster.
In simple terms, Kubernetes continuously monitors your cluster, ensuring everything is running smoothly. If something goes wrong (e.g., a container crashes), it will automatically replace it. Kubernetes also knows how to distribute containers across your nodes to ensure that no single machine is overloaded.
What Are the Main Features of Kubernetes?
By now, you’re probably seeing why Kubernetes is such a big deal. But to really understand its power, let’s explore some of its key features:
1. Load Balancing
Imagine you have an online store, and it suddenly gets a surge in traffic. Kubernetes automatically balances the load between different containers, ensuring that no single instance is overwhelmed. This ensures smooth performance for your users, no matter how much traffic you get.
2. Horizontal Scaling
Need more computing power because your app is getting more users? Kubernetes can automatically scale your app horizontally, meaning it adds more container instances to meet demand. You can scale your application up or down without any manual intervention.
3. Rollbacks and Rollouts
Every developer’s worst nightmare is deploying a bad update that crashes everything. Kubernetes has got you covered. You can easily roll out new updates or roll back to previous versions if something goes wrong. This minimizes downtime and ensures a smooth deployment process.
4. Secret and Configuration Management
Managing sensitive information like API keys or configuration settings? Kubernetes can handle that, too. It has built-in support for managing secrets and configurations securely.
5. Storage Orchestration
With Kubernetes, you can automatically mount the storage system of your choice—whether it’s local storage, public cloud providers like AWS or Google Cloud, or even network storage systems. Kubernetes helps in managing persistent storage for your applications.
Why Is Kubernetes So Popular?
There are several reasons why Kubernetes has become the go-to platform for container orchestration:
- Community Support: Being an open-source project, Kubernetes has a massive community behind it. This means continuous improvements, lots of support, and tons of learning resources.
- Cloud Agnostic: Kubernetes works on any cloud platform, allowing you to switch providers without worrying about compatibility issues.
- DevOps Friendly: Kubernetes plays nicely with DevOps tools, making it easier for teams to adopt a CI/CD pipeline and manage their infrastructure efficiently.
- Supports Microservices Architecture: As applications become more complex, the microservices architecture has become a popular design choice. Kubernetes helps manage these microservices by efficiently handling containerized workloads.
Common Use Cases for Kubernetes
You might be wondering where Kubernetes is actually used. Here are some real-world scenarios where Kubernetes shines:
1. Hosting Cloud-Native Applications
Kubernetes is ideal for running applications designed to operate in a cloud environment. It helps businesses run microservices-based applications efficiently across multiple cloud providers.
2. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Developers can use Kubernetes to automate their software deployment process. It integrates well with popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, allowing seamless deployments and updates.
3. Big Data Processing
Handling big data requires scaling, which is one of Kubernetes’ strengths. Many organizations use Kubernetes to process and analyze large datasets in real time.
How to Get Started with Kubernetes
Getting started with Kubernetes may seem a bit daunting, but don’t worry! Many cloud providers offer managed Kubernetes services, which handle much of the heavy lifting for you. These services include:
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
You can start by learning Docker and containers since Kubernetes builds on top of container technology. After that, try setting up a small Kubernetes cluster on your local machine using a tool like Minikube. Minikube allows you to run a Kubernetes cluster on your local computer, which is perfect for learning and experimentation.
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, you can dive deeper into more advanced features like Helm (a package manager for Kubernetes) or Istio (a service mesh that adds security, observability, and traffic management to your Kubernetes cluster).
It’s also helpful to go through official Kubernetes documentation and tutorials. The community is strong, and you’ll find plenty of resources to guide you along the way.
Challenges of Using Kubernetes
While Kubernetes is an incredibly powerful tool, it’s not without its challenges. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
1. Complexity
Kubernetes has a steep learning curve, especially for beginners. Understanding how all the components work together can take time. However, once you get the hang of it, the rewards are worth it.
2. Overhead
Running Kubernetes can introduce some operational overhead. Managing clusters, nodes, and the control plane can be resource-intensive, especially in smaller setups. However, managed Kubernetes services from cloud providers can significantly reduce this burden.
3. Security
Because Kubernetes is a complex system, there are several areas that can potentially be exploited if not configured properly. It’s important to follow security best practices, such as properly managing secrets and using network policies to restrict communication between services.
4. Monitoring and Logging
Keeping track of what’s happening inside your Kubernetes cluster can be difficult. You’ll need proper logging and monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana to ensure you’re aware of any issues before they become major problems.
Despite these challenges, Kubernetes’ benefits far outweigh its drawbacks for most organizations. The flexibility and scalability it offers make it a go-to solution for managing containerized applications.
The Future of Kubernetes
Kubernetes is not going anywhere anytime soon. In fact, it’s continuously evolving, with new features and improvements being added regularly. The platform is already becoming the standard for container orchestration, and its adoption is only expected to grow as more businesses move to cloud-native environments.
Some areas where we expect to see further development include:
- Improved security: As the platform matures, more robust security features will likely be introduced.
- Serverless Kubernetes: The rise of serverless computing might bring about tighter integrations with Kubernetes, allowing for even more efficient resource management.
- Edge computing: Kubernetes is also making its way into edge computing environments, enabling applications to run closer to the end-user for faster performance.
In short, Kubernetes is positioned to play a major role in the future of cloud computing and modern application development.
Conclusion
So, what is Kubernetes? In a nutshell, it’s a powerful platform that makes managing containers at scale much easier. It helps automate tasks like deployment, scaling, and monitoring, allowing developers and DevOps teams to focus more on building great applications and less on managing infrastructure.
While Kubernetes can be complex at first, it offers immense benefits in terms of flexibility, scalability, and resilience, making it a go-to tool for businesses that are serious about cloud-native applications. Whether you’re just getting started or already deep in the world of containers, Kubernetes is a platform worth investing your time in.
If you’re ready to dive into Kubernetes, take it step by step. Start with understanding the basics, experiment with Minikube, and don’t hesitate to explore the various managed Kubernetes offerings available in the cloud. It may take some effort to master, but once you do, the possibilities are endless!
Thanks for reading!
%20-%20TechieRocky_20240925_042024_0000.png)